
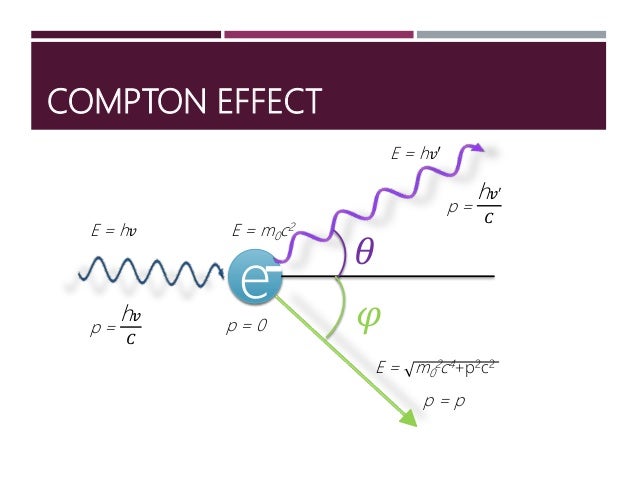
It was particularly telling that diffraction in a crystal lattice could only be explained with reference to its wave nature. “ When I presented my results at a meeting of the American Physical Society in 1923,” Compton later recalled, “ it initiated the most hotly contested scientific controversy that I have ever known.” The wave nature of light had been well demonstrated, and the idea that it could have a dual nature was not easily accepted. In his paper, Compton derived the mathematical relationship between the shift in wavelength and the scattering angle of the X-rays by assuming that each scattered X-ray photon interacted with only one electron. First postulated by Max Planck in 1900, these were conceptualized as elements of light “quantized” by containing a specific amount of energy depending only on the frequency of the light. In 1923, Compton published a paper in the Physical Review that explained the X-ray shift by attributing particle-like momentum to photons, something Einstein had invoked for his 1905 Nobel Prize–winning explanation of the photo-electric effect.

He argued that an X-ray photon can collide with an electron of a carbon atom when this happens, the photon transfers some of its energy to the electron and then continues on with diminished energy and a longer wavelength than it had before. In his new model, Compton interpreted X rays as consisting of particles, or “photons,” as he called them. Its discovery in 1922 confirmed the dual nature of electromagnetic radiation as both a wave and a particle. This discovery, known as the “Compton effect” or “Compton scattering”, demonstrated the particle concept of electromagnetic radiation, which is caused by the transfer of energy from a photon to an electron.

Compton effect video free#
In 1922, Compton found that X-ray quanta scattered by free electrons had longer wavelengths and, in accordance with Max Planck’s relation, less energy than the incoming X-rays, the surplus energy having been transferred to the electrons. His research focused on the changes that take place in the wavelength of X-rays when they collide with electrons in metals. Louis and in 1923, he moved to the University of Chicago as Professor of Physics, where he resumed his work on X-rays. In 1920, he was appointed Wayman Crow Professor of Physics, and Head of the Department of Physics at the Washington University in St. Academic CareerĪfter spending a year as instructor of physics at the University of Minnesota, Compton joined the Westinghouse Lamp Company in Pittsburgh as a research engineer until 1919, when he studied at Cambridge University as a National Research Council Fellow. Later, they would become the first such trio to simultaneously head American colleges. When Arthur Compton earned his PhD in 1916, he, and his two brothers Karl and Wilson became the first group of three brothers to earn PhDs from Princeton. Cooke, writing his dissertation on “ The intensity of X-ray reflection, and the distribution of the electrons in atoms“.

As an amateur, he purchased a telescope and photographed constellations and in 1910 Halley’s comet.In 1913, he graduated from Wooster with a Bachelor of Science degree and entered Princeton to study physics, where he received his Master of Arts degree in 1914.Compton then studied for his PhD in physics under the supervision of Hereward L. Compton was initially interested in astronomy. Elias Compton was dean of the University of Wooster, which Arthur also attended. Arthur Holly Compton – Early YearsĪrthur Holly Compton was born on Septemin Wooster, Ohio, into an academic family to Elias and Otelia Catherine Compton. It was a sensational discovery at the time: the wave nature of light had been well-demonstrated, but the idea that light had both wave and particle properties was not easily accepted. Compton won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1927 for his discovery of the Compton effect, which demonstrated the particle nature of electromagnetic radiation. On September 10, 1890, American physicist and Nobel Laureate Arthur Holly Compton was born. Arthur Holly Compton (Septem– March 15, 1962)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
