
In my opinion, a “Universal logical element” should be considered a logical element that can simultaneously perform the functions of other logical elements without changing its configuration. For example, in the general case, these are the logical elements AND, OR and NOT. In the field of digital electronics, the “Basic Logic element” is the minimum building element for creating an electronics devices operating on the basis of the laws of digital logic. For example, in the general case, for passive circuits these are RLC elements. I believe that the “Basic element of Electronics” is the minimum building element for creating an electronics device. What do You think is the difference between a “Basic logic element” and a “Universal logic element”? Please give your definition. Improved comparators distinguish between A = B = 0 and A = B = 1 states to enable better designsġ.Tutorial: Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSRs) – Part 1.
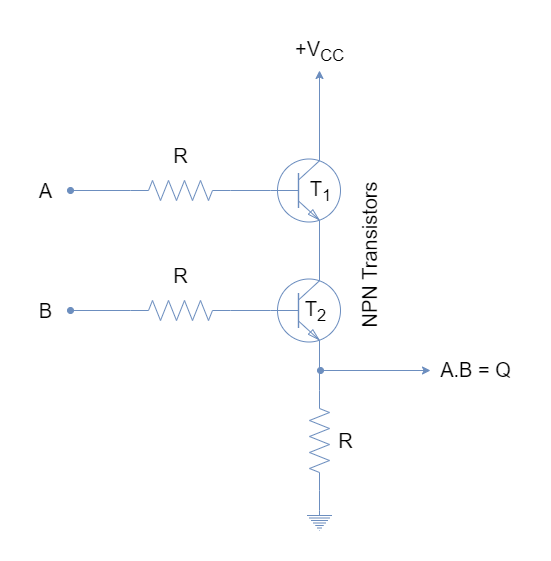
TRANSISTOR GATE TABLES HOW TO
How to invert three signals with only two NOT gates (and *no* XOR gates): Part 2.Connect passive components to logic gates.Electronic Circuits for All, London: Elektor International Media BV, 2017, 397 p. The disadvantages of passive universal logic elements include their low load capacity, the small possibility of their sequential cascading in view of the progressive loss of output voltages. The advantage of the logic elements discussed above is their exceptional simplicity, versatility of use and the ability to operate in a wide range of input voltages: from one to hundreds of volts. Table 3 RS-trigger truth table using two universal logic elements. RS-trigger based on two universal logic elements. When a short rectangular pulse is applied to the input X1 or X2, the trigger switches its state.įigures 3. Table 2 The truth table of the logical element “ONLY ONE OF TWO”.įigure 3 and Table 3 show the possibility of using two universal logic elements as an RS-trigger. įigure 2 Logical element “ONLY ONE OF TWO”.
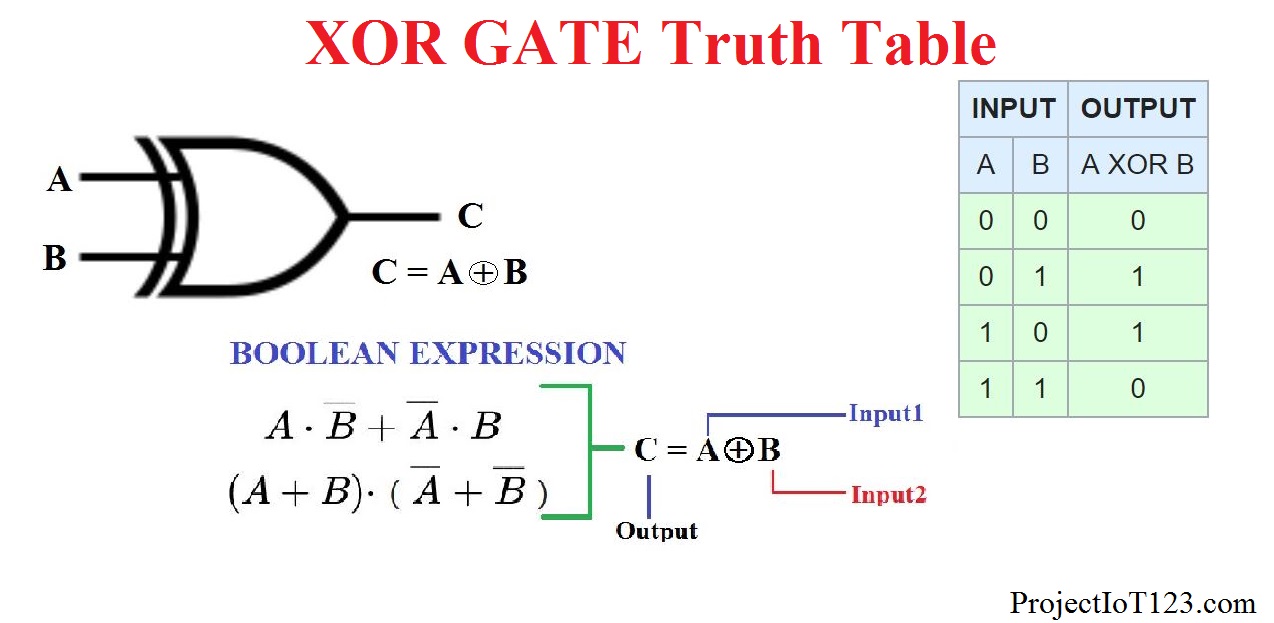
The logical element “ONLY ONE OF TWO” is a special case of the logical element “ONLY ONE OF ALL”. If two or more input signals coincide in time, the “ONLY ONE OF THE TWO” element will not pass any of them to the outputs ( Figure 2, Table 2). The logic element “ONLY ONE OF TWO” is a logic element that ensures the passage of only one of the two signals from the input of the element to its corresponding output. Let’s consider further the possibilities of using universal logical elements as a logical element “ONLY ONE OF TWO”. Similar processes, but with a minus sign, will be observed during the operation of the universal logic element of negative logic. 1”, and the output +Y2 (XOR) will have “Log. 1” is applied to both inputs +X1 and +X2, then the outputs +Y1 (OR) and +Y3 (AND) will have the levels “Log. 1” levels, and the output +Y3 (AND) will have “Log. 0”, then the outputs +Y1 (OR) and +Y2 (XOR) will have “Log. If one of the inputs +X1 or +X2 is supplied with a voltage of the “Log.

Table 1 Truth table of universal logic elements of positive and negative logic. The truth table can be seen below (Table 1). If no control signals are applied to the inputs +X1 and +X2, the outputs +Y1 (OR), +Y2 (XOR), +Y3 (AND) have logical zero levels. Figure 1 Universal logical elements of positive and negative logic.Ĭonsider the operation of the universal logic element of positive logic (Figure 1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
